Concept of DEOS
In order to achieve Open Systems Dependability, we have proposed the concepts of the following three_items;
- DEOS Process
- DEOS Architecture
- D-Case
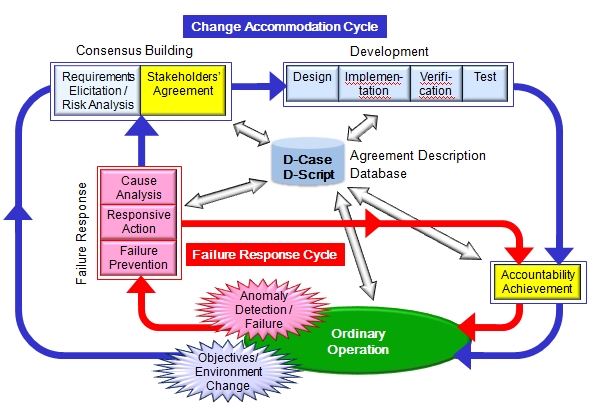
1. DEOS Process
An iterative process, which consists of the followings is indispensable.
- A cycle to adapt the system according to changes in objectives and environment
- A cycle to take immediate actions and fix failures when they occur
The process, which consists of these two cycles, is a Process of Processes composed of component processes and states
- These processes are organically united
DEOS Process
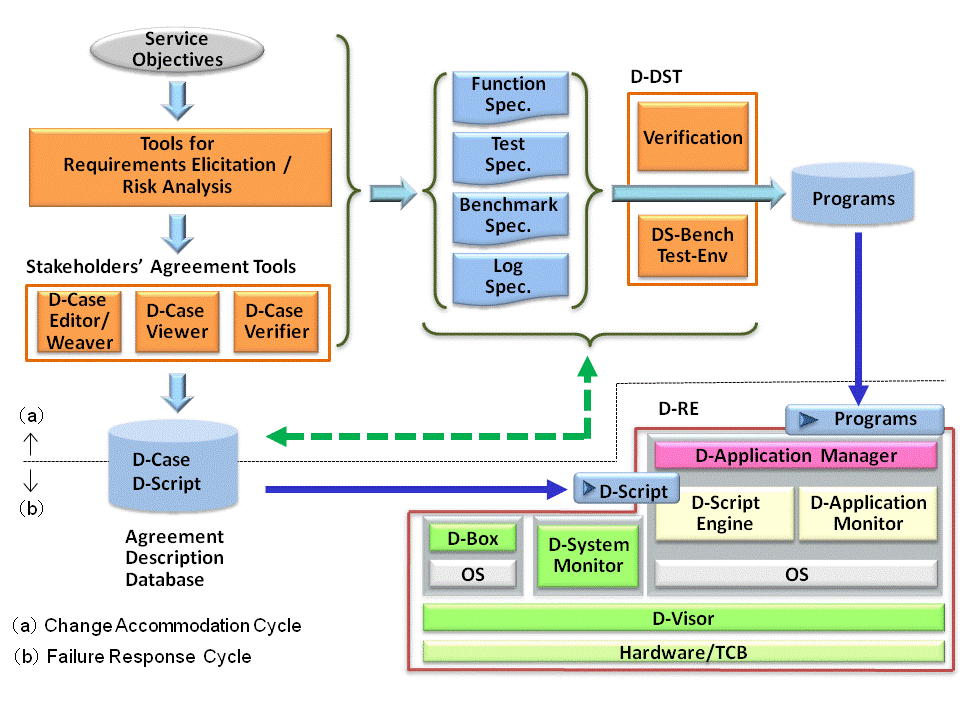
2. DEOS Architecture
In order to apply the DEOS process to systems, an architecture that can effectively support the DEOS process is required.
We think that key components of this DEOS architecture include;
- A set of tools to support the requirements elicitation/risk analysis phase, and database to store agreement and the process to reach agreement
- A set of tools for program verification, benchmarking, and fault injection test, and
- A runtime environment to monitor the system all the time, to record and report events, and to react dynamically to minimize the damage to the services when failure occurs.
We named the architecture as "DEOS Architecture".
DEOS Architecture
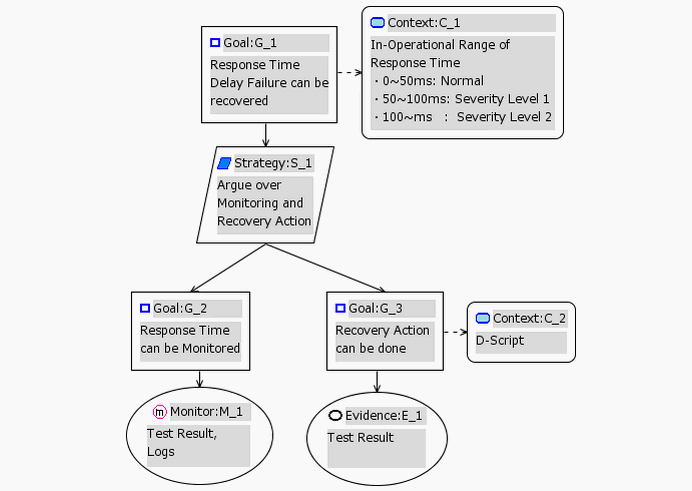
3. D-Case
The largest benefits to be gained by using the "DEOS Process" are that sufficient agreement can be carried out leading to agreement after the stakeholders have change their demands and that reasoning / argument that reached the agreed-upon results / conclusion.can be recorded. We named this consensus building method "D-Case", and also call the agreement document produced based on the agreement descriptions "D-Case".
By clearly and completely describing the following four points, "D-Case" offers the framework for building a more firmly based argument.
- Claim
- Argumentation
- Evidence
- Explicit Assumption
D-CASE